Does your B2B data enable you to effectively utilise the GDPR advantage?
If you don’t have an immediate answer to that, you are already late. Of course, you have taken all the measures to get complied. But does your ROI benefit from the on-going changes? Admit it – the impeccable lead quality thanks to GDPR comes at a trade-off to dipping lead volumes and burdening lead generation costs. Even the top ranking organisations have begged to ask: are the returns worth it?
It turns out: they are.
- Better lead quality and relevance means average deal size will increase.
- GDPR’s customer-centric model will automatically increase buyer trust.
- Stiff regulatory hurdles will filter out huge chunks of competition, keeping the market fresh and needy for your services.
GDPR doesn’t unbalance the playing field. It merely gives your prospects a fair chance to play in it.
8 Important GDPR Compliance Instruments for Your B2B Data
With playoffs just a month ahead, you need to have a few things ready at hand. It’s easy enough to acquire.
What You Need:
- Information Asset Register
- LIA Report
- DPIA Template
- Explicit Consent Template
- Automation Workflow Blueprint
- Information Security Policy
- Data Access Point
- Data Protection Team
Get Your Data Assets Complied with Our Expert Assistance. Enquire Now!
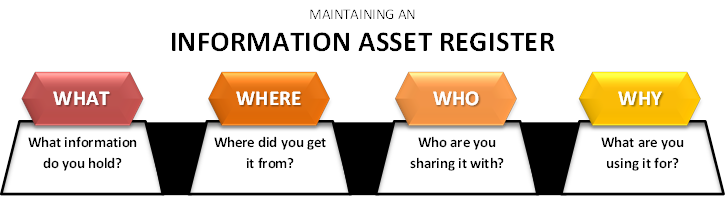
#1: Information Asset Register
A good database leaves its trails. A great database records it. Regular data auditing is a good way to track the health of your B2B data and check its current compliance status. Under GDPR, knowing your data through-and-through is a requisite and a major roadblock if not adhered to.
Your information audit should be able to answer the following questions comprehensively, and in detail.
Ask yourself:
- What data I hold and why do I need it?
- How do I collect the data?
- Where is the data stored, and how?
- What do I do with the data?
- Who owns and controls the personal data?
- What are the policies regarding retention and deletion of data?
- Who is responsible for the data and processors associated with data?
- Do I have adequate technology to adequately manage data processing?
A B2B data audit report can also act as a cornerstone to build your business strategies around it. Records need to be maintained progressively of all audits hosted on the particular database.
UK’s top data protection authority, the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) suggests businesses to maintain a dynamic register, containing the ‘who’, ‘what’, ‘why’, and ‘where’ of your database on a real-time basis – an Information Asset Register.
#2: LIA Report
GDPR recognizes 6 lawful bases for processing personal data (any information that identifies the subject as an individual, e.g.: personal mail IDs as well as Individual official mail IDs):
- Consent: the individual has given clear consent for you to process their personal data for a specific purpose.
- Contract: the processing is necessary for a contract you have with the individual, or because they have asked you to take specific steps before entering into a contract.
- Legal Obligations: the processing is necessary for you to comply with the law (not including contractual obligations).
- Vital Interests: the processing is necessary to protect someone’s life.
- Public Tasks: the processing is necessary for you to perform a task in the public interest or for your official functions, and the task or function has a clear basis in law.
- Legitimate Interests: the processing is necessary for your legitimate interests or the legitimate interests of a third party unless there is a good reason to protect the individual’s personal data which overrides those legitimate interests.
Source: Data Protection Self-Assessment, ICO
For businesses at large, the most practical choices are: through extracting an explicit consent, and through establishing a legitimate interest for processing the data.
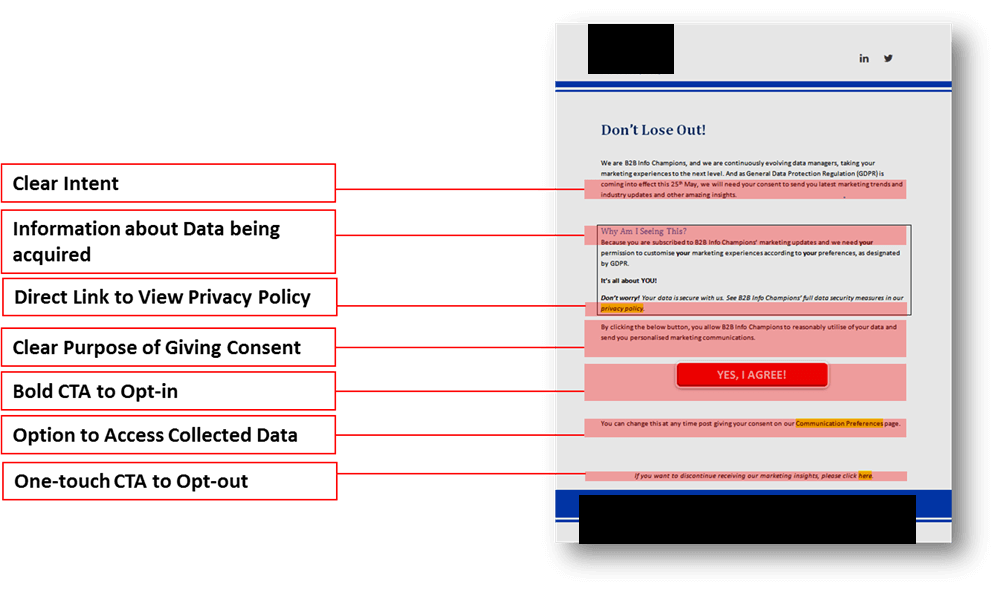
Generating explicit consent for business purposes is still a vulnerable area as GDPR rules are extremely stringent in this regard. And there is also the risk of losing massive portions of their historical data in case of low open rates in opt-in campaigns (the average open rates of business emails is around 25%).
Legitimate interest, on the other hand, stands out for its flexibility and recognition of goodwill in the business’ past data handling activities. To establish a concrete legitimate interest, regulators define a three-part test, also called Legitimate Interest Assessment (LIA).

Identity Test:
Conduct a thorough investigation of your business operations to identify the legitimate interest(s). Consider:
- Why do you want to process the data – what are you trying to achieve?
- Who benefits from the processing? In what way?
- Are there any wider public benefits to the processing?
- How important are those benefits?
- What would the impact be if you couldn’t go ahead?
- Would your use of the data be unethical or unlawful in any way?
Necessity Test:
Identify loopholes in your “interest” and figure out all alternate routes (that require limited processing or no processing of data) to achieve it. This is in reference to the ‘privacy by design’ (data usage minimisation) concept introduced in GDPR. Consider:
- Does this processing actually help to further that interest?
- Is it a reasonable way to go about it?
- Is there another less intrusive way to achieve the same result?
Balancing Test:
Analyse the impact of your processing and whether it overrides your “interest” or the data subjects’ rights. Consider:
- What is the nature of your relationship with the individual?
- Is any of the data particularly sensitive or private?
- Would people expect you to use their data in this way?
- Are you happy to explain it to them?
- Are some people likely to object or find it intrusive?
- What is the possible impact on the individual?
- How big an impact might it have on them?
- Are you processing children’s data?
- Are any of the individuals vulnerable in any other way?
- Can you adopt any safeguards to minimise the impact?
- Can you offer an opt-out?
Know More About Compliance Assistance Model. Find Out Now!
#3: DPIA Template
Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) is an essential and handy tool to judge the security threats that each processing activity inherently poses. According to GDPR (Article 35), applying new technologies especially in processing activities increases the risk of conflicting freedoms and interests of data subjects.
Thus, to mitigate such high-risk scenarios, a standard DPIA template must be available with all controllers. The DPIA should disclose the following information:
- Description of the nature, scope, context and purposes of the processing and, where applicable, the legitimate interests pursued by the business
- Assessment of the necessity and proportionality of the processing in relation to the purpose
- Objective assessment of the risks to individuals, which considers both the likelihood and severity of the possible harm
- Controls identified to address the risks, and whether those risks (including information security) are eliminated, reduced or accepted as a result
- A special focus on ‘residual risk’ (unmitigated risk factors post the assessment) need to be provided also at the end
Active involvement of the DPO to conduct the DPIA is thoroughly advised.
#4: Explicit Consent Template
Clarity is the keyword when it comes to consent in GDPR. No more short fonts, complex jargons, and lengthy forms while collecting opt-in permissions! Data subjects have more control on the private data they want to share under GDPR.
- Data collection consent forms have to be intelligible and clearly distinguishable from all other types of declarations asked from the subject, and cannot be combined with other information notices.
- Privacy policies surrounding data collection and processing (tenure of storage, purpose of storage etc.) have to be more detailed and easily accessible.
- Enterprises will be obliged to maintain records to show the collection source, collection media, purpose and explicit consent of the data subjects for the entire tenure of storage.
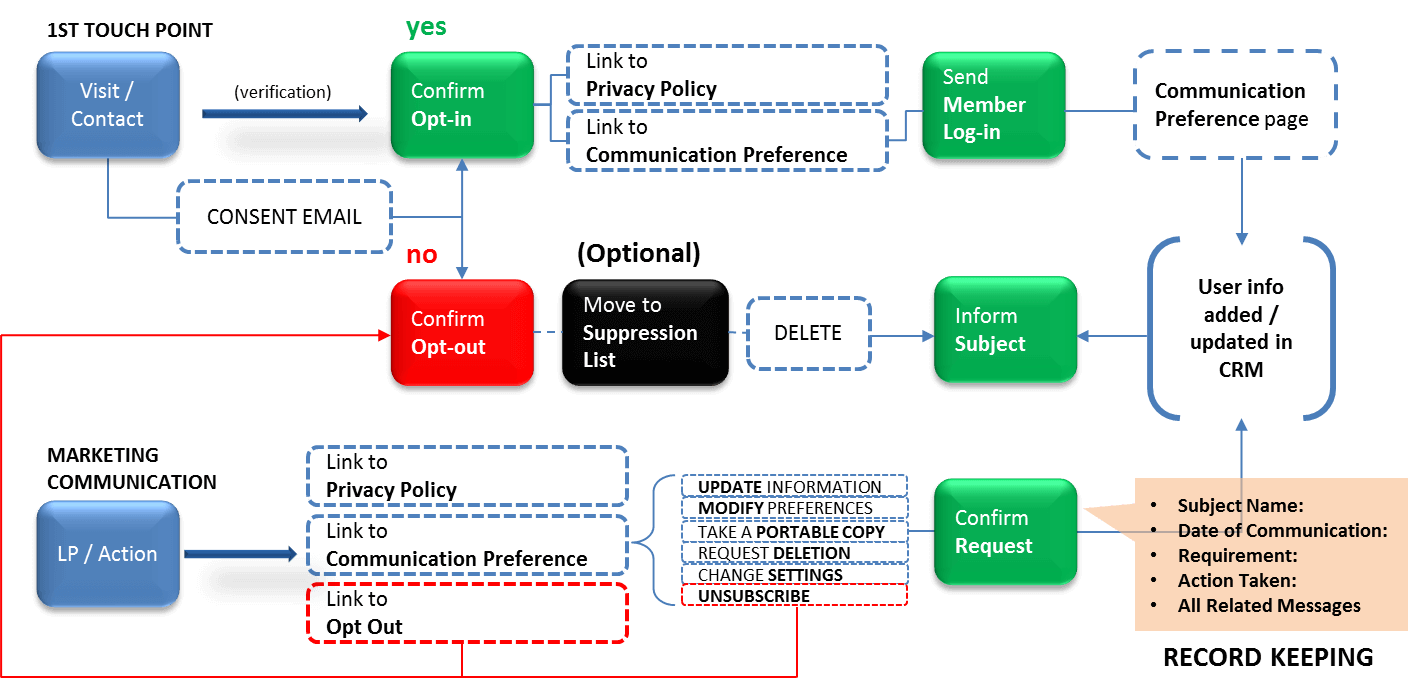
#5: Automation Workflow Blueprint
Maintaining instantaneous responses across thousands of data points every day requires automation. But proper alignment to the regulatory framework across different automation funnels is also necessary. To maximise the gains from such automation, a clear workflow needs to be present.
Controllers/Processors require automation in:
- Consent Management
- Record Management
- Communications & Responses
- Breach Notification
#6: Information Security Policy
Security of personal information and commitment to user privacy is what GDPR is all about. Each controller and processor needs to stand up to this task. Apart from a secure privacy policy, controllers need to also come up with a concrete information security policy. The policy can at least include the following points:
- Subject Rights (Article 12 – 23; GDPR)
- Responsibility of Controllers and Processors (Article 24, 25, 29-35; GDPR)
- Regulatory Codes of Conduct (Article 40; GDPR)
- General Data Transfer Principles (Article 44; GDPR)
Credibility of the information security policy is supreme during registration with the regional supervisory authorities in EU. The controllers and processors are also obliged to present it in the situation of a data breach investigation.
Assuring Information Security:
- Risk Analysis: Analyse risks that are posed by processing the data. The resulting report can be used as guidance while formulating the information security measures.
- Cost Analysis: While deriving the tools to effect security, the kind of technology to be used and their costs have to be taken into account.
- Multi-Level Strategy: Apart from the main security policy, other policies (privacy policies, client contracts, user controls etc.) would also have to reflect the commitment towards secure data practices.
- Encryption: Processors need to apply encryption and/or pseudonymisation (hiding parts of the complete datum) where necessary.
- Regular Updates: The organisation’s data security principles and controls have to be reviewed, tested, and updated regularly, and as demanded by the kind of data they possess.
- Restoration: Processors must have the technology available to restore access to personal data in case of such access is lost. Example: by establishing a viable backup mechanism.
- Code of Conduct: Controllers and processors must understand their requirements of confidentiality, integrity and availability of their possessed data. Certification processes are implemented at junctures where necessary.
#7: Data Access Point
Complying with the ‘Right to Access’ clause (article 15) in GDPR, “The data subject shall have the right to obtain from the controller confirmation as to whether or not personal data concerning him or her are being processed, and, where that is the case, access to the personal data…”.
“Access” to personal data can be provided through a simple membership page.
- Provide the user a member log-in to your site after collecting their consent.
- Add a ‘preferences’ page inside the membership portal. This page can contain:
- Brief introduction about your business, and your objective to collect the data
- A marketing profile of the user, comprising of editable tabs with user’s personal data available with you. Add an ‘Export’ button at the end to give them a portable copy of the data.
- A ‘communication preferences’ column with checkboxes of all relevant communications (not pre-checked) that the user may choose to be sent to them.
- Link to the privacy policy page to give them relevant information about the usage of their data.
- Clear and bold options to unsubscribe or opt out from their consent.
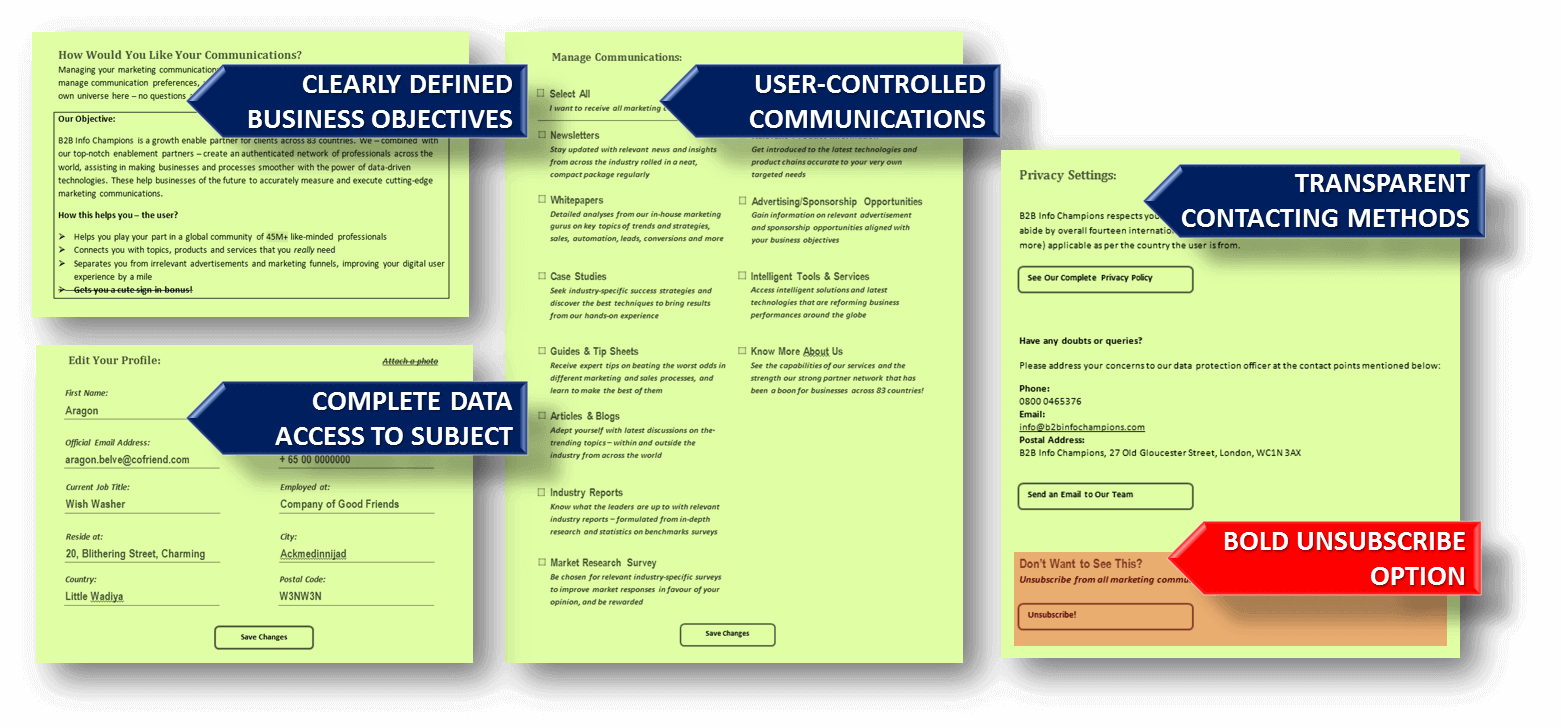
Despite the regulatory factors, the ‘Preferences’ page is also a unique platform that can promote transparent user-business engagement, and influence buyer trust.
#8: Data Protection Team
The last and most important instrument for excellence is your compliance team, led by your chosen Data Protection Officer (DPO).
Instead of going back and forth on obtaining permits from local Data Protection Authorities (DPAs), GDPR keeps the onus of record keeping within the controllers and processors. Such organisations, with core operations relating to “regular and systematic monitoring of data subjects on a large scale”, will have to appoint DPOs to fulfil their data protection duties.
Duties of the Data Protection Officer:
- Inform and advise controllers and/or processors about obligations pursuant to GDPR and other Union and Member State laws regarding data protection.
- Monitor the organisation’s compliance to GDPR and other data protection laws, by…
- Assigning responsibilities to the compliance team and other employees involved in data processing activities
- Raising awareness within the organisation through staff training and other activities
- Hosting related information audits periodically
- Advice and supervise Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) when necessary.
- Act as the organisation’s point of contact with data protection authorities to consult on issues regarding processing and relevant matters.
DPOs will not be liable to obtain approvals from DPA related data processing activities under the Model Contract Clauses (MCCs).
The time couldn’t have been more right for GDPR – a subject-centric model of data protection. It clearly defines the risks, and imposes the onus of compliance on the businesses themselves. The world needs GDPR, and this trend is here to stay! Businesses should be prepared. The playing field is levelling… globally.
Need assistance in your GDPR Compliance? Need a fast-track solution? We have the best route for you! Contact Span Global Services’ data experts today.
KNOW BEFORE OTHERS!